A. Indications for gestational surrogacy -
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS), bandaid surgery,
or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen
are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) as opposed to the larger
incisions needed in laparotomy. Keyhole surgery makes use of images displayed on
TV monitors to magnify the surgical elements.
Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities,
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus
an open procedure. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions and hemorrhaging,
and shorter recovery time.
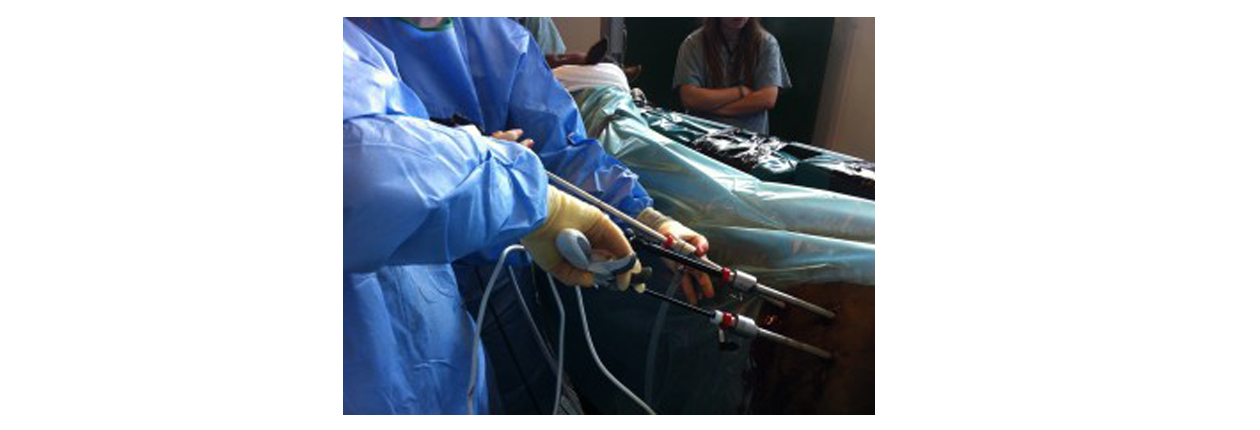
The key element in laparoscopic surgery is the use of a laparoscope. a digital laparoscope
where the charge-coupled device is placed at the end of the laparoscope, Also attached
is a fiber optic cable system connected to a ‘cold’ light source (halogen or xenonto
illuminate the operative field, inserted through a 5 mm or 10 mm cannula or trocar
to view the operative field. The abdomen is usually insufflated, or essentially
blown up like a balloon, with carbon dioxide gas. This elevates the abdominal wall
above the internal organs like a dome to create a working and viewing space. CO2
is used because it is common to the human body and can be absorbed by tissue and
removed by the respiratory system. It is also non-flammable, which is important
because electrosurgical devices are commonly used in laparoscopic procedures.
B. Procedure -
Laparoscopy is done by a gynecologist surgeon. General anesthesia is generally used, but other types of
anesthesia, such as spinal anesthesia, may be used. About an hour before the surgery, you will empty your
bladder. You will get fluids and medicine through an intravenous (IV) in a vein in your arm. You may get
a medicine (sedative) to help you relax..
Several procedures may be done after you get your anesthesia and are relaxed or asleep.
- 1. An airway will be placed in your throat to help you breathe if you get general anesthesia.
- 2. A thin flexible tube (urinary catheter) may be put through your urethra into the bladder.
- 3. Your surgical area will be washed with a special antiseptic solution.
During laparoscopy, a small incision is made in the belly. More than one incision may be made if other tools
will be used during the surgery. A hollow needle is put through the first incision and gas (carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide)
is slowly put through the needle to inflate the belly. The gas lifts the abdominal wall away from the organs inside so your
doctor can see clearly. A thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) is then put through the incision to look at the organs. Other tools
can be used to take tissue samples, fix damage, or drain cysts. After the surgery, all the tools will be removed and the gas
will be released. The incisions will be closed with stitches and covered with a bandage. The scar will be very small and will
fade over time
Laparoscopy takes 30 to 90 minutes, depending on what is done, but can take longer if a condition (such as endometriosis)
is found and treated. After the laparoscopy, you will go to the recovery room for 2 to 4 hours. You can usually do your normal
activities the next day, but do not do any strenuous activity or exercise for about a week.